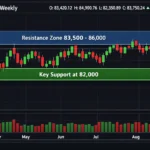
What Is Sensex? A Simple Guide to India’s Market Pulse
what is Sensex, Sensex is the heartbeat of India’s stock market. If you follow business news or track investments, you’ve probably seen headlines saying “Sensex jumps 500 points” or “Sensex crashes amid global worries.” But what exactly is Sensex, and why does it matter so much?
In this detailed guide, we explain what is Sensex, how it works, its history, and why millions of investors rely on it to understand the mood of the Indian stock market.
Why Is Sensex So Important?
Sensex matters because it reflects:
- Overall mood of the Indian stock market
- Investor confidence in the economy
- Performance of top companies across sectors
- Impact of global events on Indian markets
For many investors, Sensex is the first number they check every morning to know how the market is doing.
Who Manages Sensex?
The Sensex is managed by Asia Index Pvt Ltd, a subsidiary of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). The index committee regularly reviews and updates the companies included to ensure Sensex truly represents India’s economy. BSE, established in 1875, is Asia’s oldest stock exchange and is regulated by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), ensuring transparency and trust.
How Does Sensex Work?
Sensex is calculated using the free-float market capitalisation method.
What does that mean?
It considers:
- Share price of each company
- Number of shares available for public trading
- Weight of each stock in the index
This method ensures Sensex reflects only the shares actively traded in the market, not promoter-held shares.
Simple Formula:
Sensex = (Total Free-Float Market Cap / Base Market Cap) × Base Value
The base year is 1978–79, with a base value of 100.
What Does a Rising or Falling Sensex Mean?
- Sensex rising -> Investors are optimistic, companies performing well.
- Sensex falling -> Worries about economy, inflation, global cues, or poor earnings.
Even a 100-point move can make headlines, though today Sensex levels are above 70,000, showing how much India’s market has grown.
Brief History of Sensex
Sensex was introduced on January 1, 1986, making it India’s first stock market index.
Key Milestones:
- 1990s: Liberalisation era brings market boom
- 2008: Global financial crisis, Sensex crashes
- 2021: Crosses 60,000 mark
- 2024–25: Touches record highs above 75,000 (intraday)
Sensex has grown from 100 to over 70,000+, reflecting India’s economic journey.
Which Companies Are in Sensex?
Sensex consists of 30 blue-chip companies from sectors like:
- Banking & Finance
- IT
- Oil & Gas
- FMCG
- Metals
- Automobiles
- Pharmaceuticals
These are industry leaders with strong financials and large market value.
We’ll cover the full list in detail in our upcoming article:
“What Are the 30 Shares in Sensex?”
How Are Companies Selected for Sensex?
Companies must:
- Be listed on BSE
- Have high liquidity
- Large free-float market cap
- Strong trading history
- Represent key sectors of the economy
The list is reviewed periodically to keep Sensex relevant.
Sensex and the Indian Economy
Sensex often mirrors India’s economic health.
- Growth in GDP-> Sensex tends to rise
- High inflation or interest rates-> Pressure on Sensex
- Political stability-> Boosts investor confidence
- Global crises-> Can drag markets down
That’s why Sensex reacts instantly to:
- RBI policy announcements
- Union Budget
- US Fed decisions
- Geopolitical tensions
Who Should Track Sensex?
Sensex is useful for:
- Long-term investors
- Traders
- Mutual fund investors
- Business readers
- Students of finance & economics
Even if you don’t invest directly, Sensex helps you understand market sentiment.
Can You Invest in Sensex Directly?
You cannot buy Sensex itself, but you can invest through:
- Index mutual funds
- ETFs based on Sensex
- Futures & options (derivatives)
These instruments aim to replicate Sensex’s performance.
Read Now
“What Is Sensex Futures?”
“How to Trade in Sensex Options?”
Sensex vs Individual Stocks
Instead of betting on one company, Sensex gives you exposure to:
- Multiple sectors
- Top companies
- Lower risk compared to single stocks
That’s why many experts suggest index investing for beginners.
Why Sensex Is Called the Market Barometer
Just like a thermometer checks temperature, Sensex checks market health.
A steady rise means:
- Corporate profits are growing
- Economy is stable
- Investors are confident
A sharp fall signals:
- Panic selling
- Economic worries
- Global shocks
Sensex in Daily News
You’ll often read headlines like:
- “Sensex jumps 800 points on banking rally”
- “Sensex slips amid weak global cues”
These moves are driven by:
- Company earnings
- Global markets
- Crude oil prices
- Rupee movement
- Foreign investor flows
Common Myths About Sensex
X Sensex rising means everyone is making money
_/ Not true. Only stocks in the index may be rising.
X Sensex fall means economy is collapsing
_/ Markets react to short-term news too.
X Sensex is only for experts
_/ Anyone can track and understand it with basics.
Is Sensex Reliable?
Yes. Sensex is:
- Transparent
- Regulated by SEBI
- Managed by BSE professionals
- Based on scientific calculation
It’s globally respected and tracked by foreign investors too.

Sensex and Long-Term Wealth Creation
Historically, Sensex has delivered 12–15% average annual returns over the long term, despite ups and downs.
This shows:
- Power of compounding
- Importance of patience
- Strength of India’s growth story
Many mutual funds benchmark their performance against Sensex.
Sensex for Beginners: Key Takeaways
If you’re new, remember:
- Sensex = India’s top 30 companies
- Shows market direction
- Moves daily based on news & earnings
- Useful for tracking, not panic
Understanding Sensex is your first step into stock markets.
What’s Next in Our Sensex Series?
To build a complete knowledge cluster, we’ll cover:
- What was the Sensex in 1990?
- What are the 30 shares in Sensex?
- Difference between Nifty and Sensex
- What is Sensex futures?
- How to trade in Sensex options?
About the Author
This article is written by a market researcher who closely follows Indian equities and financial trends, using data from BSE, SEBI, and public financial reports to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what is Sensex is essential for anyone interested in India’s financial markets. More than just a number, Sensex tells the story of India’s economy, investor confidence, and corporate growth.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned investor, keeping an eye on Sensex helps you stay connected to the country’s economic pulse.
Reviewed for accuracy and last updated on December 24, 2025.